carbonyl structural formula Carbonyl group biology ap writework
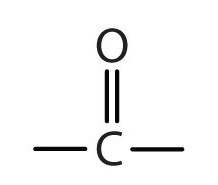
Carbonyl compounds are a fascinating and important subset of organic chemistry. They are defined as a compound that contains the carbonyl functional group, which consists of a carbon double-bonded to an oxygen atom. Carbonyl compounds include many important classes of molecules, such as aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids. The structure of the carbonyl group is essential to understanding the properties and reactions of carbonyl compounds. The carbon-oxygen double bond in the carbonyl group is polar, with the oxygen atom being more electronegative than the carbon atom. This polarity gives carbonyl compounds many of their characteristic properties, such as their ability to form hydrogen bonds and undergo nucleophilic addition reactions. One way to visualize the structure of the carbonyl group is to look at the resonance forms of the molecule. The carbon-oxygen double bond can be thought of as being partially double and partially single, with the electrons being delocalized between the two atoms. This delocalization leads to the formation of two resonance forms, which have slightly different properties. The first resonance form has a double bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms, with the oxygen atom having a formal negative charge. This form is more stable than the second form, as the negative charge is on the more electronegative oxygen atom. The second resonance form has a single bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms, with the carbon atom having a formal positive charge. This form is less stable than the first form, as the positive charge is on the less electronegative carbon atom. The properties of carbonyl compounds depend on the relative stability of these two resonance forms. For example, the nucleophilic addition reaction of an alcohol with a carbonyl compound involves the formation of a hemiacetal intermediate, which is stabilized by the second resonance form. The final product of this reaction is a cyclic acetal, which is more stable than the hemiacetal due to the combined stabilization of both resonance forms. Overall, carbonyl compounds are essential to organic chemistry due to their unique properties and importance in biological systems. The structure of the carbonyl group is fundamental to understanding these compounds and their reactions, and visualizing the resonance forms of the molecule can aid in this understanding.
If you are searching about 17.2: Structure of the Carbonyl Group - Chemistry LibreTexts you’ve came to the right place. We have 5 Images about 17.2: Structure of the Carbonyl Group - Chemistry LibreTexts like 14.9: Aldehydes and Ketones- Structure and Names - Chemistry LibreTexts, Carbonyl Definition in Chemistry and also 17.2: Structure of the Carbonyl Group - Chemistry LibreTexts. Read more:
17.2: Structure Of The Carbonyl Group - Chemistry LibreTexts
 chem.libretexts.orgcarbonyl ketone group structure hydrogen ketones aldehydes bonding why reaction sn2 chemical oh resonance partial charge dipole octet carbon structures
chem.libretexts.orgcarbonyl ketone group structure hydrogen ketones aldehydes bonding why reaction sn2 chemical oh resonance partial charge dipole octet carbon structures
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS | Organic Chemistry Quiz - Quizizz
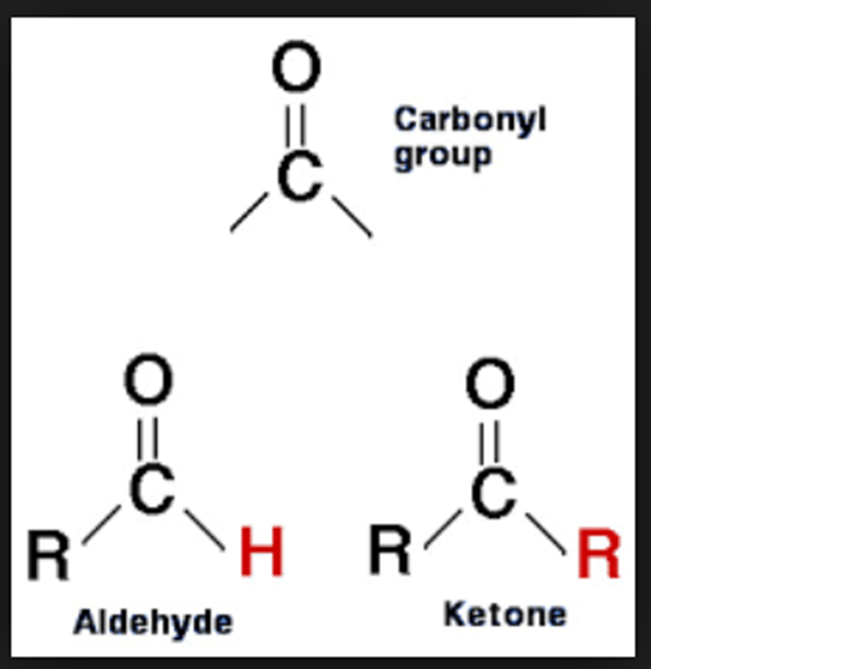
Ap Biology Notes. - WriteWork
 www.writework.comcarbonyl group biology ap writework
www.writework.comcarbonyl group biology ap writework
14.9: Aldehydes And Ketones- Structure And Names - Chemistry LibreTexts
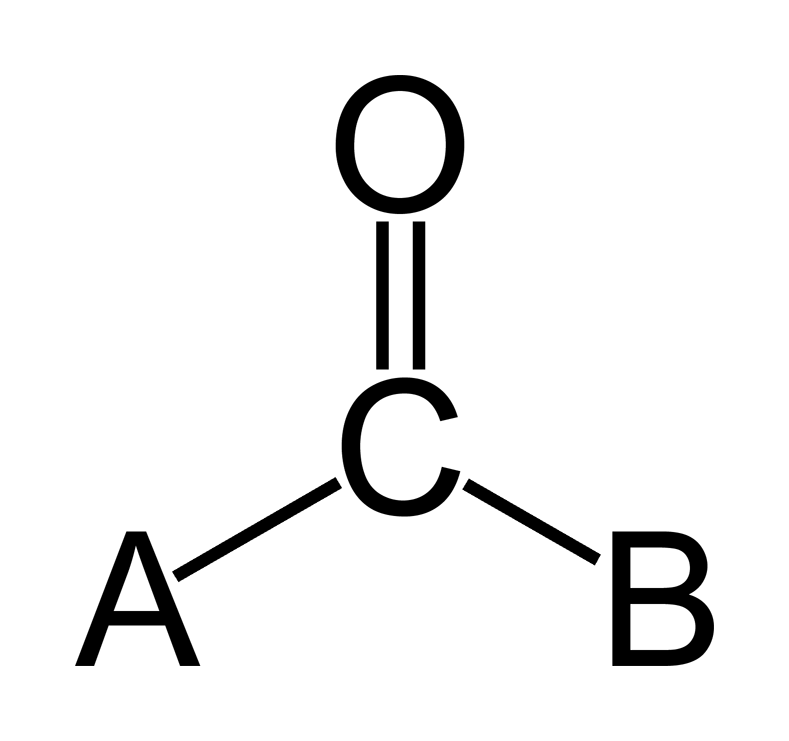
 chem.libretexts.orgcarbonyl group structure chemical ketones aldehydes names formula structural compounds organic chemistry chem groups libretexts carbon life blocks chapter building
chem.libretexts.orgcarbonyl group structure chemical ketones aldehydes names formula structural compounds organic chemistry chem groups libretexts carbon life blocks chapter building
Carbonyl Definition In Chemistry
/carbonylfunctionalgroup-56a129e03df78cf772680058.jpg) www.thoughtco.comcarbonyl definition chemistry
www.thoughtco.comcarbonyl definition chemistry
Carbonyl compounds. Carbonyl group biology ap writework. Carbonyl compounds quizizz chemistry organic